Asia is a leading region both in sugar production and sugar consumption. This key region is made up of many countries, and we will be focusing on two of the major players, Thailand and China, in this blog. The full series, covering Japan, South Korea, The Philippines, Indonesia, Vietnam and Malaysia can be found on Czapp for free.
Thailand’s raw sugar industry
Thailand is one of the world’s largest raw sugar exporters and an especially important supplier to East Asian refiners.
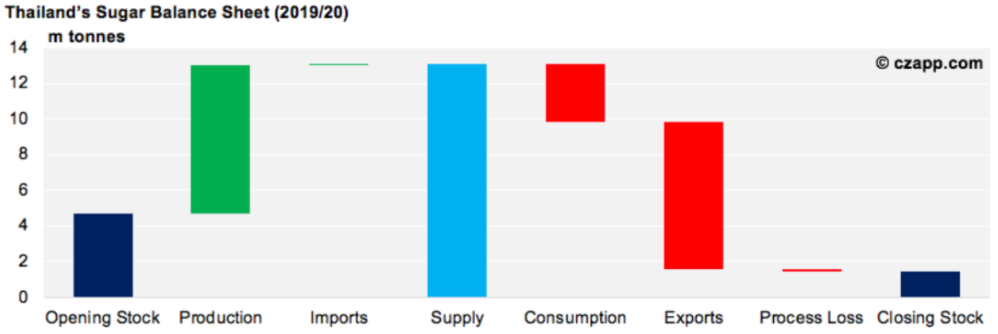
Around 50% of Thailand’s raw sugar is produced in the North-East of the country, and is then transported to ports in the South via truck. The major sugar ports are the Aow Thai Terminal, Kerry Siam Sea Port, and Siam Commercial Sea Port, located at Laem Chamang and Sri Racha.
Thailand’s raw sugar is often highly competitive on the world market because Thai mills are efficient and have a low cost of production. In recent years, most of Thailand’s raw sugar has been exported to Indonesia, as the country has a large sugar deficit and strong demand for its refining sector.
Thailand’s white sugar industry
Thailand is also a major white sugar producer and exporter. We explain the difference between white and raw sugar in our sugar series.
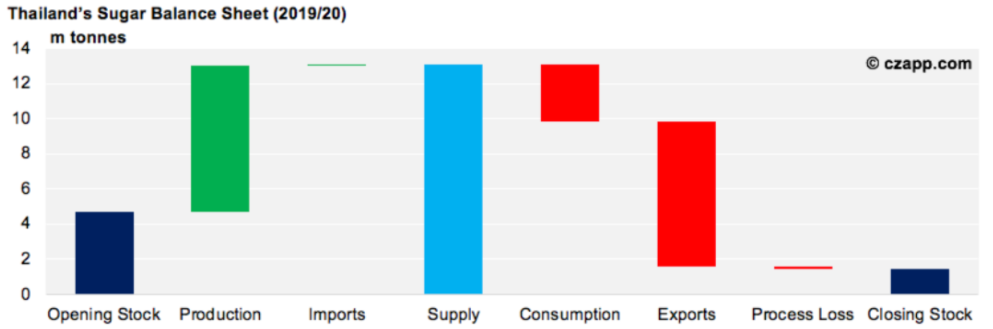
Thailand makes white sugar directly from sugar cane, but also by re-melting raw sugar at the end of the cane crushing season. By law, Thai mills must produce enough white sugar each year to satisfy domestic demand.
People in Thailand are becoming more aware of the amount of sugar they consume, in part because the government increased its soft drinks tax in 2018. The remaining sugar can then be exported, predominantly to countries in South East Asia.
China’s sugar market
China is one of the world’s largest sugar consumers, and also one of the world’s largest importers of raw sugar.
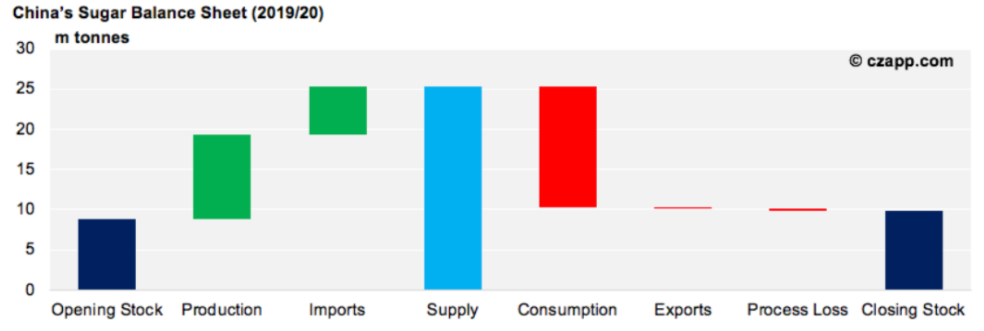
Chinese sugar production peaked at 14.84 million tonnes in 2007/08, and has lingered at around 10 million tonnes ever since, meaning China’s sugar consumption has outstripped production and the country is regularly in deficit.
The local sugar mills’ inability to meet consumption has created a space for the sugar refining sector, processing imported raw sugar. The refineries operate in a protected environment: government licences are required to build a refinery, the refineries’ raws processing capacity must be approved by the Ministry of Commerce (around once a year) and permits are required to import raw sugar once the refinery is operational.
Despite the country’s economic growth and rapid urbanisaton over the past decade, China’s sugar consumption is relatively stable, with most of the growth in sweetener consumption having been captured by high fructose corn syrup (HFCS) in the last 10 years.
For more information about the global sugar market you can visit Czapp to read more about each key region, along with all the information you need on the market more generally. There are many free articles, and premium content for more specific, in-depth analysis.
Looking To Buy Sell Or Move Sugar?



