History of the Thickener
Food thickeners are frequently based on either polysaccharides (starches, vegetable gums and pectin), or proteins. These ingredients serve the sole purpose of thickening the consistency of a product. Czarnikow trades different thickeners: Corn and tapioca starch, xanthan gum, CMC and pectin.
Corn starch was discovered in 1840 by Thomas Kingsford. He used a process called ‘wet-milling’, which involved soaking corn kernels in an alkaline substance before grinding them. This was based on Orlando Jones’ extraction of vegetable starch. Until 1851 corn starch was primarily used for starching laundry, however when its edible, thickening properties were discovered, cookbooks began to publish recipes that included corn starch. The great benefit of corn starch is that it is completely tasteless, so it has the ability of thickening food without interfering with its flavour.
Xanthan gum received its name from a species of bacteria used during the fermentation process, Xanthomonas Campestris. It was first invented by Allene Rosalind Jeanes at the United States Department of Agriculture in the early 1960’s. The polysaccharide (or if you’re feeling less fancy the carbohydrate whose molecules consist of a number of sugar molecules) is prepared by the bacteria being placed into an aqueous solution of carbohydrates, dipotassium phosphate, nitrogen, and of course, some trace elements. Once the xanthan polymer forms extracellularly into the medium, isopropyl alcohol is added and the polymer precipitates, dries, and is milled to form a powder – pretty simple really.
CMC was first discovered by E.Jansen in early twentieth century Germany, and uses one of the world’s most common organic materials, cellulose, which is found in the cell walls of all plants. CMC (also known as carboxymethyl cellulose or cellulose gum) is a cellulose derivative made from the alkali-catalyzed reaction of cellulose with chloroacetic acid. This reaction results in a mixture that is 60% CMC and approximately 40% salts, commonly used in detergents. To create pure CMC the mixture undergoes an additional purification process, which can then be used in various food applications. To thicken, stabilise and retain moisture.
Pectin is naturally occuring and was first isolated by Henri Braconnot in 1825. During the ninteenth century, makers of jam and preserves used apple juice to extract pectin. Later however, it was commercially produced in a similar manner but from citrus peel. It was first sold as a liquid, but is now more commonly sold as a dry powder as this makes it easier to ship and store.
The Current Market
The plot thickens… corn starch currently accounts for 80% of global starch production, of which 40.92% is used in the food and beverage sector. Its market size is estimated to be $17.02 billion in 2019, but its growing thick and fast, with a CAGR of 8.2%, and an estimated $29.39 billion market size by 2026. This is potentially owing to the increase in demand for sweeteners, for which corn starch is a fundamental ingredient. North America, being the largest producer of the thickener, has the largest market share and is expected to grow the most with a forecast CAGR of 8.57%. The Asia Pacific region is also expected to see growth, owed to the increase in demand of snack products.
The xanthan gum market is different (thicker) gravy. It is currently estimated to be worth $857 million, growing at a CAGR of 5.9%, thus reaching an estimated $1.076 billion by 2023. Currently, the Asia Pacific region dominates the market in both volume and value, and this area is expected to grow the most in the future. This can be attributed to the rapid urbanization in countries such as China or Indonesia, and the accompanying rise in demand for processed food.
Corn Starch – Product Overview

Corn starch is a white, free flowing powder, and can be slightly altered to suit the preference of the manufacturer. It’s used as a thickening agent in soups, sauces, pasta, confectionary and beer.
- Fineness: 99.94% through a 180 μm mesh (#80 mesh code)
- Fat Content: 0.2% Max
- MUST be negative for Salmonella and E. coli.
- Supplied in: Double ply paper 25kg bags; Polypropylene 25kg bags; Jumbo bags multiwall 1000kg.
- Shelf Life: 24 months
- Storage: 25- 35oC
Common Applications
Corn starch is commonly used in baked goods, confectionary, beverages, soups, sauces, gravies and dairy products.
Fun Facts
- Corn starch has many alter egos: Maizena, maize starch and corn flour.
- Corn starch is frequently used in bath bombs.
- Corn Starch companies included trading cards in their packaging as a form of advertising. These cards soon became incredibly valuable.
Xanthan Gum – Product Overview

Xanthan Gum is often used in baking, and helps food retain more moisture due to its ability to stabilise emulsions. It’s often found in batter, because it helps it cling onto food that is about to be fried. It does not lose its properties when microwaved, so you can take it out of your microwave and it’ll be ready to thicken, all gums blazing. It also can add a texture to your sauce that only fat could otherwise do, so it is perfect for low-fat meals.
- Shelf Life: 36 Months
- Storage: Stored in a cool and dry place and kept away from strong light and heat.
- CAS #: 11138-66-2
Variations
- 40 Mesh food grade
- 80 Mesh food grade
- 80 Mesh European
- 200 Mesh food grade
- 200 Mesh European
- Xanthan Gum XD
- Xanthan Gum RD
Common Applications
Xanthan gum is commonly found in sauces, ice cream, toothpaste, egg substitutes. Baked goods, dairy products, beverages.
Health Benefits
There are several health benefits to xanthan gum. To name a few, it helps to fight cancer by boosting the immune system, It can also decrease glucose concentrations, lowerblood pressure, fights tooth decay, and can help to control hunger. It has been known to treat osteoarthritis and dry mouth. This list of benefits is by no means exhaustive, there are many more known health benefits associated with the consumption of xanthan gum.
Fun Facts
- Xanthan gum is also an emulsifier, helping ingredients stay blended, like oil and vinegar
- Xanthan gum only makes up around 0.5% of the food’s weight. Thick things come in small packages.
- It is also used in ice cream to prevent it from crystallising and keeping it smooth.
CMC – Product Overview
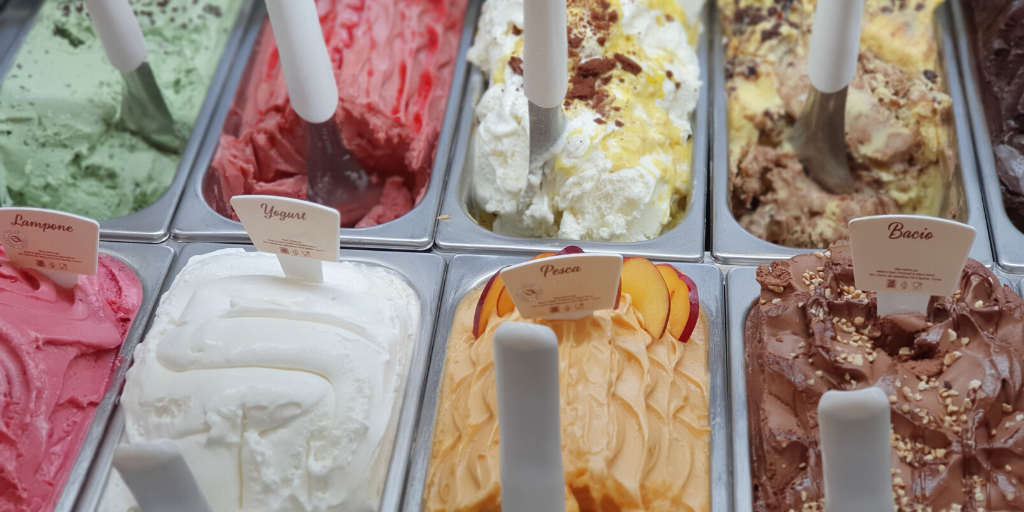

CMC is used in food as the E number E466 or E469 across a range of products including ice cream. CMC has a high viscosity, meaning it is highly resistant to deformation. This attribute makes it very useful in helping manufactured food keep its thickness, texture and shape. It allows for a cheaper manufacturing process, eliminating the need for alternative fats or egg in baked goods and extreme freezing in the creation of ice cream. The lower quantities of fat and dairy needed also make CMC very popular for use in diet and low-fat foods.
Shelf Life: 12 months
Storage: < 35 oC in a clean, dry, well ventilated warehouse away from odours.
Purity: >99.5% pure
Health Benefits
As mentioned above, CMC can help reduce the intake of fats, and it may help supress the appetite.
Fun Facts
- CMC also has many non-food applications, such as toothpaste, detergents, heat packs and paint.
- CMC has film forming properties, meaning it’s commonly used in pills
- CMC is made from cellulose, which can be found in all plants.
Pectin – Product Overview

Unlike the above products, Pectin is a naturally occuring thickener. It is a type of starch (or heteropolysaccharide if you’re feeling fancy), and is present in the cell walls of fruit and vegetables. In plants, it helps to add structure, and in food it can do the same thing as an ingredient.
Varieties
- High Methoxyl (HM) – this is the most common type of Pectin, and is frequently labelled as ‘fast-set’. This is because – you guessed it – it sets fast.
- Low Methoxyl (LM) – this is also known as ‘slow-set’, and sets slower.
- Pectin is available as a liquid or solid dry powder
- It also comes as a low or no sugar variety
Common Applications
Pectin is a gelling agent, and can is therefore a very useful thickener. It is used across a range of products such as jellies, yoghurts and juices, but is most famously used in jams and preserves.
Health Benefits
Unlike gelatine, pectin is vegetetarian so can be used to make animal-free products. It has also been used for some medicines as it is not toxic.
Fun Facts
- Some fruits have higher pectin levels than others – for example citrus fruits.
- Pectin is from the Greek ‘pektikos’, meaning ‘congealed’
- Acid is used to draw pectin out of the fruit
If you’d like to find out more about thickeners, or any of the other ingredients we supply, please contact us.
Author: Carys Wright
Photographers: Brooke Lark, Lama Roscu, Ben Ashton